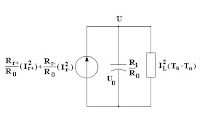
and thermal models which interact as diagrammed in Figure 1. In the
electrical model, the voltage, V, and the slip, S, determine the rotor
current. The summation of all torques acting on the motor shaft
comprises the mechanical model. Here, the driving torque developed
by the motor is resisted by the load torque and the moment of inertia
of all the rotating elements, all of which are slip dependent. The thermal
model is the equation for heat rise due to current in a conductor
determined by the thermal capacity, the thermal resistance, and the slip
dependent I2R watts. As the ultimate protection criteria, the thermal
model is used to estimate the rotor temperature, U, resulting from the
starting condition with initial temperature U0. A recursive solution using
finite time increments is used because the rotor impedance changes
continuously with slip.

Figure 1: Motor Analysis Block Diagram
Index
Index
1. DEFINING THE ELECTRICAL MODEL